Pharmacist who reads papers
Healthy immunity without overabundance, take care of it with 'this'
1. Maintains
immune system health2. Relieves
inflammatory and autoimmune diseases3. Prevents inflammatory diseases

Hello. I'm a pharmacist Jinny.
As the daily temperature has increased to around 10 degrees, the transition season has begun, when immunity tends to decline. It's not just because it's springtime, but I think a lot of people are concerned about their immunity these days.
A healthy immune system is defined as a state in which there is no deficiency or excess of an immune response. The immune system is a complex mechanism that regulates the body's response to external threats and internal disorders, and a lack of an immune response can lead to a loss of resistance to foreign antigens, and if it is excessive, it can cause a chronic inflammatory response, which can lead to tissue damage and loss of physical functions.
Today, I would like to introduce an ingredient that normalizes the function of the immune system by performing anti-inflammatory functions in the body and alleviates the chronic inflammatory response caused by the overactive immune system. It's the omega-3 you're familiar with.
1. Maintain immune system health
Ever since studies showed that Greenlanders, who consume enough omega-3s, have lower cholesterol levels and lower rates of heart disease, even though they don't eat a lot of vegetables, the scientific community continues to study the benefits of omega-3 supplementation. Among them, the effect of omega-3s in preventing autoimmune diseases has been consistently reported.
In January 2002, Isr Med Assoc J published a meta-study that comprehensively reviewed existing papers on omega-3s. This study evaluates the role of omega-3s in the prevention of autoimmune diseases caused by overactive immune responses [1].
"Continued consumption of omega-3 fatty acids may inhibit any autoreactive (or hyperreactive) T cells, contributing to a reduction in the incidence of inflammation and autoimmune diseases. (Omitted) The use of omega-3 fatty acids may be recommended to prevent the risk of autoimmune diseases.”
2. Alleviates inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
Omega-3 supplementation has been reported to help prevent autoimmune diseases, and research has continued to assess whether omega-3 levels of anti-inflammatory effects can function in autoimmune diseases and the resulting severe inflammatory diseases.
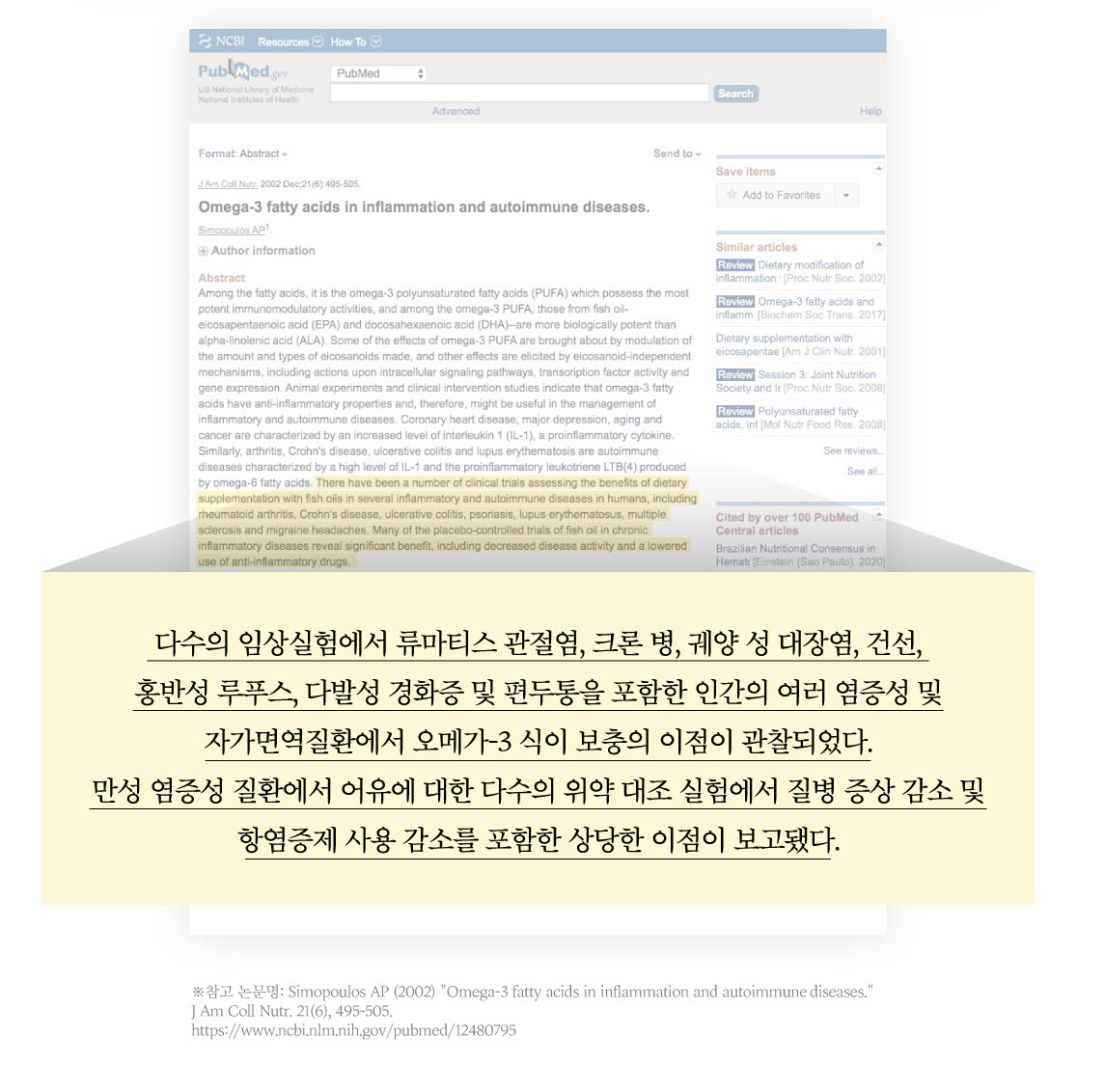
In December 2002, J Am Coll Nutr published the results of a meta-study that reviewed animal and clinical intervention studies on omega-3s. This paper evaluates the role of omega-3s in relieving symptoms of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases of varying severity [2].
"Numerous clinical trials have observed the benefits of omega-3 dietary supplementation in several inflammatory and autoimmune diseases in humans, including rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and migraine. In chronic inflammatory disease, a number of placebo-controlled trials of fish oil have reported significant benefits, including reduced disease symptoms and reduced use of anti-inflammatory drugs."
3.Prevention of inflammatory diseases
As shown in the previous study, the anti-inflammatory mechanism of omega-3 is caused by the mechanism by which the immune response is suppressed. As a result, studies have been conducted to determine whether the anti-inflammatory effect of omega-3 can be maintained even against inflammation that is not caused by an overimmune response.
In 2014, PLOS ONE published a study that conducted a comprehensive analysis of clinical studies of omega-3s from 1950 to 2013. This study sheds more detail on the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of omega-3s and evaluates their function [3].
"Our study suggests that supplementation with marine-derived n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) may effectively prevent inflammation-related chronic diseases, considering its significant degradation effects on CRP (C-reactive protein), IL-6 (interleukin-6), and TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor α) in healthy subjects. The anti-inflammatory effect is most effective in non-obese patients, and in conclusion, marine-derived n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation has a marked lowering effect on TNF-α, IL-6 and CRP in fasting blood."
That's a brief overview of the scientifically validated functions of omega-3s.
I hope you have a healthy day in body and mind. It was Jinny.
[1] Ergas D, Eilat E, Mendlovic S, Sthoeger ZM (2002) "n-3 fatty acids and the immune system in autoimmunity" Isr Med Assoc J., 4(1), 34-38
[2] Simopoulos AP (2002) "Omega-3 fatty acids in inflammation and autoimmune diseases." J Am Coll Nutr. 21(6), 495-505.
[3] Li K, Huang T, Zheng J, Wu K, Li D (2014), Effect of marine-derived n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on C-reactive protein, interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor α: a meta-analysis., PLOS ONE, 9(2), e88103.






![[Oyster Extract (FGO) Efficacy] Oyster Extract, a New Key for My Child's Height Growth](http://esther-mall.com/cdn/shop/articles/82.jpg?v=1734067861&width=480)

Comments (0)
There are no comments for this article. Be the first one to leave a message!