If you are at an age where you are aging, you should pay attention to coenzyme Q10.
high blood pressure2. Improves
blood sugar control

Hello. I'm a pharmacist Jinny.
Aging of the body is a human fate that neither I nor you who are reading this article can avoid. In general, our body begins to deteriorate at the age of 30, and by the time we reach our mid-40s, our joints and muscles · Signs of aging are felt, especially in the eyes, and as the overall function of the organs decreases, the body's resistance to external stressors weakens, making it increasingly vulnerable to disease.
The level of deterioration of organs with aging depends on how well the cells in them are functioning, and when cells are active, the level of deterioration decreases.In other words, there are no specific signs of aging. That's why coenzyme Q10, the ingredient we're going to introduce today, is said to be one of the most important anti-aging nutrients.
Coenzyme Q10 is a nutrient that plays an essential role in the functioning of mitochondria, the energy factories in cells, while also protecting cells through its antioxidant activity. The benefits of taking it have also been studied from various angles, and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety has recognized Coenzyme Q10 as a functional ingredient for blood pressure and antioxidants, and the academic community has also recognized it as a functional ingredient for aging and aging. Adult diseases · We continue to report benefits for cardiovascular disease.
Today, we will take a look at how coenzyme Q10 can contribute to the prevention of aging in our body through academic research on coenzyme Q10, a representative anti-aging nutrient.
According to the National Health Insurance Corporation, the number of hypertension patients in Korea last year was 13.74 million. This means that 1 in 4 adults over the age of 20 have high blood pressure, which is a condition in which the pressure in the arteries is abnormally high, and it is not only a major cause of aging of blood vessels, but also a phenomenon of aging blood vessels. It can also lead to complications such as angina, myocardial infarction, and cerebrovascular disease.
The antihypertensive benefits of coenzyme Q10, a leading anti-aging nutrient, have been reported to the scientific community since 1994. P Langsjoen and the researchers (1994) evaluated the effect of coenzyme Q10 intake on blood pressure in 109 patients with essential hypertension and reported that improvements in systolic and diastolic blood pressure were confirmed.
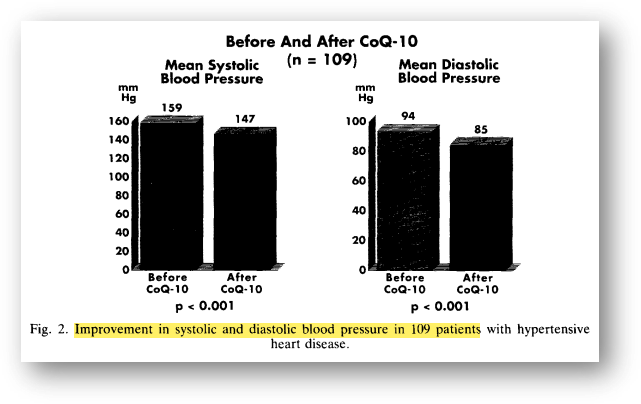
"Overall NYHA (New York Heart Association) functional ratings improved from an average of 2.40 to 1.36 (P<0.001), and 51% of patients completely discontinued 1~3 antihypertensive medications at an average of 4.4 months after starting CoQ10."
Among the functions that decline with age is the ability to regulate blood glucose levels. In particular, it is known that after the age of 5 or 0 years, theability to control blood sugar after meals steadily decreases every 10 years. This phenomenon has been interpreted as a result of a combination of factors such as increased visceral fat mass, loss of muscle mass, and decreased insulin sensitivity associated with biological aging [2].
Recently, however, it has been hypothesized that age-related mitochondrial dysfunction in cells is the root cause of poor blood sugar control. As a result, the benefits of coenzyme Q10, an important nutrient for mitochondrial function, in glycemic control were evaluated. A clinical trial in 50 diabetics reported the benefits of coenzyme Q10 in improving glycemic control.

"The results of this study show that 12 weeks of supplementation with coenzyme Q10 can improve glycemic control in diabetics, regardless of their lipid profile."
Loss of muscle mass, which was previously cited as one of the causes of the decline in blood sugar control due to aging, is also a natural part of aging. Muscle mass tends to decline steadily from the age of 30 onwards, so experts always suggest that exercise is the basis for maintaining good health. However, the deterioration of cardiopulmonary function, muscular, and skeletal system function due to aging is also a factor that makes it difficult to exercise.
As one of the leading anti-aging nutrients, CoQ10 is also known to affect exercise performance. Cooke, M, and the investigators who evaluated the effects of single or continuous intake of coenzyme Q10 on exercise performance report that coQ10 intake improved exercise performance in both aerobic and anaerobic exercise.
"Continuous supplementation with coenzyme Q10 increased plasma coQ10 concentrations and increased the duration of exercise when feeling exhausted. These results indicate that supplementation with coenzyme Q10 affects exercise performance in different types of exercise."
Today, we learned about coenzyme Q10, a representative anti-aging nutrient. It has many benefits for blood pressure and blood sugar, which we need to pay attention to as we age, as well as exercise performance, so if you have ever felt older, please pay attention to it.
In addition, if you are taking CoQ10, it is recommended that you take it after meals rather than on an empty stomach, and in the morning or during the day rather than in the evening. In addition, most clinical trials evaluate the intake for 6 months, so it is important to consume it consistently.
I hope you have a healthy day in body and mind. It was Jinny.
[1] P Langsjoen, P Langsjoen, R Willis, K Folkers. (1994) Treatment of essential hypertension with Coenzyme Q10. Mol Aspects Med. 15:S265-72.
[2] DeFronzo, R. A. (2004). Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medical clinics, 88(4), 787-835.
[3] Zahedi, H., Eghtesadi, S., Seifirad, S., Rezaee, N., Shidfar, F., Heydari, I., ... & Jazayeri, S. (2014). Effects of CoQ10 supplementation on lipid profiles and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial. Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders, 13(1), 1-8.
[4] Cooke, M., Iosia, M., Buford, T., Shelmadine, B., Hudson, G., Kerksick, C., ... & Kreider, R. (2008). Effects of acute and 14-day coenzyme Q10 supplementation on exercise performance in both trained and untrained individuals. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 5(1), 8.


![[CoQ10 Efficacy] 3 Effects of CoQ10 to Prevent Free Radicals, the Main Cause of Aging](http://esther-mall.com/cdn/shop/articles/2_c6871298-563e-4f40-8006-7b0f46147d63.jpg?v=1733983067&width=480)


Comments (0)
There are no comments for this article. Be the first one to leave a message!