Apple cider vinegar, improves diet efficiency.
diet efficiency2. Weight and blood sugar reduction

Hello. I'm a pharmacist Jinny.
I'm not a big advocate for whole-food hygiene purposes. It is true that there are beneficial ingredients in natural foods, but since they have not been refined, the content of the active ingredients is low, so you need to consume an excessive amount of them in order to consume them sufficiently, which can lead to adverse effects due to excessive consumption.
However, the natural food that changed my mind is apple cider vinegar. In fact, when I first started my academic review of apple cider vinegar, I had a negative mindset, thinking, "Even if it is a food prescribed by Hippocrates, will it be effective enough to be verified in empirical studies?"
Apple cider vinegar, also known as apple cider vinegar, refers to the traditional vinegar obtained by naturally fermenting apple juice, not the liquor fermented brewed vinegar that we can easily find in supermarkets. Unlike the modern method of rapid fermentation in 1~2 days, fermentation and aging are carried out for a long time because apple juice becomes cider under the influence of fermentation strains and gradually turns into apple cider. As a result, it has a different microbiota and chemical composition than ordinary vinegar.
Today, I would like to introduce the results of a human application study on apple cider vinegar, the protagonist who broke my prejudice against natural foods.
When we feel the need to lose weight, the first thing we try is diet, especially calorie-restricted diets, which reduce the amount of calories we consume, are arguably the most routine diet regimens in the world. However, if calorie restriction alone doesn't have a special effect on your diet, you may want to try apple cider vinegar before lunch and dinner.
In a 2018 study published in the Journal of Functional Foods assessing the effects of apple cider vinegar consumption on a calorie-restricted diet, the test group alone consumed one tablespoon (15 ml) of apple cider vinegar at lunch and dinner and found significant reductions in body weight, BMI, hip circumference, visceral fat index (VAI), and appetite compared to the control group [1].

"Consumption of apple cider vinegar significantly reduced body weight, BMI, hip circumference, visceral fat index (VAI) and appetite scores (P ≤ 0.00). In addition, plasma triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) levels were significantly reduced in the apple cider vinegar group compared to the control group, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations were significantly increased (P ≤ 0.05)."
When we go on a diet, we limit calories, but we try to eat as few carbs as possible and mainly proteins and vegetables. In fact, the reason this diet is so important is that refined carbohydrates are associated with a rapid rise in blood sugar. When blood sugar rises rapidly in the body, insulin is secreted excessively and glucose is stored as fat, resulting in an increase in body fat.
As such, there are studies that show that apple cider vinegar is helpful for blood sugar control, which is inseparable from weight and body fat management, so I would like to introduce it. In 2019, Drug Invention Today published a study in a clinical trial that evaluated the benefits of apple cider vinegar in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity with high insulin resistance. In this study, a little more than one tablespoon (20 ml) of apple cider vinegar was consumed before bedtime for 30 days, and blood sugar levels and weight loss were reported [2].
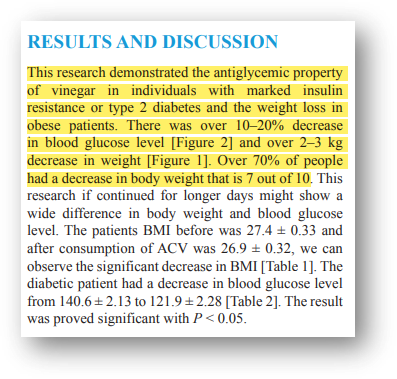
"This study demonstrates the inhibitory properties of apple cider vinegar for insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes and weight loss in obese patients. A reduction in blood sugar level of 10~20% and a weight loss of more than 2~3kg were observed by consuming apple cider vinegar, and 70% of test subjects experienced weight loss."
I mentioned earlier that when blood sugar rises rapidly in the body, insulin is secreted excessively and glucose is stored as fat, and in general, this process causes blood sugar to drop back to normal levels. However, when insulin is secreted and blood sugar does not drop, it is called insulin resistance (IR). It is a type of insulin resistance caused by a constant rise in blood sugar, in which case high blood sugar is maintained, which increases the likelihood of developing metabolic diseases.
In 2004, the scientific community reported the results of a clinical trial that evaluated the effects of apple cider vinegar consumption in non-diabetics and type 2 diabetics with high levels of insulin resistance. In this study, participants were given a drink diluted with 20 g of apple cider vinegar diluted in water just before a meal, and all apple cider vinegar groups showed significant improvement in insulin sensitivity compared to the control group [3].
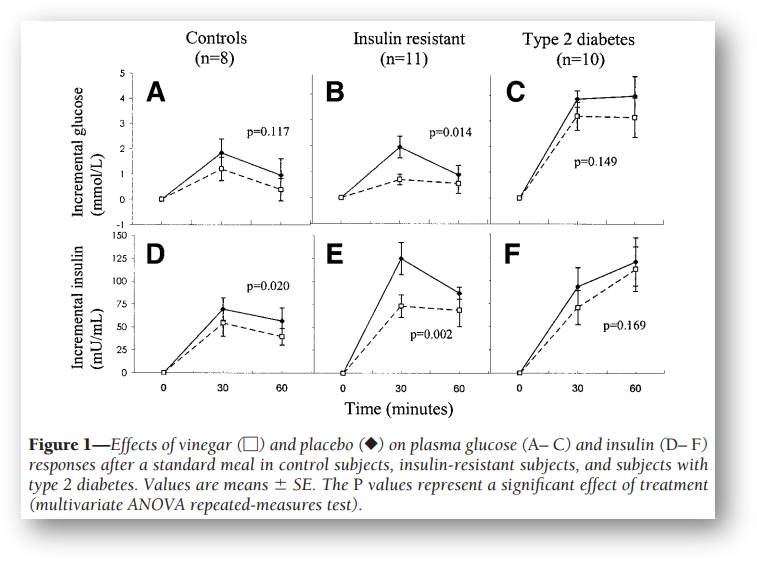
"Consumption of apple cider vinegar increased systemic insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant subjects 60 minutes after eating (34%, P > 0.01, paired t test) and a significant improvement in insulin sensitivity (19%, P > 0.07) was observed in patients with type 2 diabetes."
Today, I reviewed the human application studies of apple cider vinegar, a beneficial natural food that many of you may have known about earlier than I did. It is not just a food that helps with weight loss, but also affects insulin sensitivity, blood sugar, and appetite control, and as a result, it helps to lose weight, so it is a good idea to use it when you are dieting or worried about insulin resistance.
In addition, when reviewing the research, I found that the daily intake was not as high as I expected, and it was usually recommended to take one tablespoon (15ml) 1~2 times a day, diluted with water and taken right before meals. Basically, it is a food with high acidity, so when consuming it, it is best to refer to the dosage in the human application test and consume it safely.
I hope you have a healthy day in body and mind. It was Jinny.
[1] Solaleh Sadat Khezri(2018). Beneficial effects of Apple Cider Vinegar on weight management, Visceral Adiposity Index and lipid profile in overweight or obese subjects receiving restricted calorie diet: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Functional Foods 43, 95-102.
[2] Pusparatha, S. B., Devi, R. G., & Jyothipriya, A. (2019). Effects of apple cider vinegar on diabetic and obese patients. Drug Invention Today, 12(5).
[3] Johnston, C. S., Kim, C. M., & Buller, A. J. (2004). Vinegar improves insulin sensitivity to a high-carbohydrate meal in subjects with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. Diabetes care, 27(1), 281-282.


![[Apple cider vinegar benefits] 3 benefits of apple cider vinegar to improve diet efficiency](http://esther-mall.com/cdn/shop/articles/33.jpg?v=1733993412&width=480)
![[Calcium Benefits] 3 hidden benefits of calcium that are essential for diet](http://esther-mall.com/cdn/shop/articles/32.jpg?v=1733993146&width=480)
![[Immunity BEST 5] Basics of Health, Ingredients for Immunity BEST 5](http://esther-mall.com/cdn/shop/articles/34.jpg?v=1733993679&width=480)
Comments (0)
There are no comments for this article. Be the first one to leave a message!