
Vitamin D is not found in many of the foods that modern humans eat. It is found in blue fish, mushrooms, milk, butter, eggs, etc., but only at an insignificant level. The foods with the highest vitamin D content per unit gram are animal intestines, including liver. Primitive man had no reason to be deficient in vitamin D. Primitive man ran around with his bare skin exposed in the sun, hunted animals, and ate their entrails whole. However, modern man does not like to expose his skin to the sun for cosmetic reasons or because of skin cancer.
The National Institutes of Health recommends that the best way to synthesize vitamin D is to expose your face or limbs directly to the sun at least twice a week between 10 a.m. and 3 a.m., for at least 20 minutes at a time, without sunscreen. In this case, about 200 IU of vitamin D is produced. Exposure to the sun, which causes erythema in the middle of summer, can produce 10,000 IU of vitamin D, but prolonged exposure to strong UV rays is not good for skin health. In summer, it is recommended to bask in the sun 2~3 times a week, before 11 am or after 4 pm. However, this is a level that prevents a deficiency of vitamin D.
Even if a sunscreen has a sun protection factor (SPF) of more than 80,000, the skin will hardly synthesize vitamin D. However, the sunscreen cream you use should have at least SPF 15. In addition, vitamin D synthesis occurs through UVB rays, which have a shorter wavelength than UVA, which has a longer wavelength than UVA. UVB rays do not pass through glass, so vitamin D cannot be synthesized in a room trapped inside glass, even if you are exposed to sunlight. This means that it is difficult for modern humans to synthesize enough vitamin D through their skin.
Nor can we force them to eat animal intestines. Butter is high in saturated fat, so I don't eat dairy products because it hurts my stomach, and I don't eat blue fish often because it's hard to bake. Shiitake mushrooms, which are known to be rich in vitamin D, are rarely sun-dried these days, and most of them are hot air dried. Hot air dried mushrooms contain less vitamin D. Cooking and blanching also cause vitamin D loss. As a result, unlike other vitamins, vitamin D intake through food is only about 100IU, about 10~20% of the recommended daily intake.
That is why the lack of vitamin D in modern man is at an acute level. The U.S. fortified cereals and milk with vitamin D to prevent rickets for more than 20 years. Despite such efforts, blood levels of vitamin D in Americans remain low. According to data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Examination in the United States, in 2010, 42 percent of Americans were deficient in vitamin D blood levels of less than 20 ng/ml.
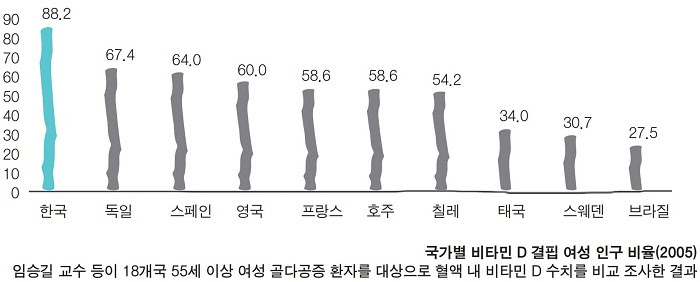
In our country, the situation is much worse. According to a 2014 survey conducted by the Seoul Institute of Medical Sciences, 86% of adolescents aged 18~20 and 71.1% of the adult population had vitamin D blood levels below 20ng/ml. According to the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service in 2011, more than 16,000 people with vitamin D deficiency were treated by doctors. In 2005, a multi-center international study conducted by Professor Seung-Gil Lim of Yonsei University School of Medicine and others found that among adult women from 18 countries around the world, Korean women ranked last in blood vitamin D concentration. Even the vitamin D deficiency of Korean women was worse than that of women in the Middle East, who wore chadors all their lives. It's hard to believe, but in the late Joseon Dynasty and the Japanese colonial era, newborns with rickets are often born in the delivery rooms of major university hospitals in recent years. Women in our country This is because they don't eat properly due to their usual diet, and they block too much sunlight for fear of skin aging. If the mother lacks vitamin D in her blood, the fetus's bones are bent and born.
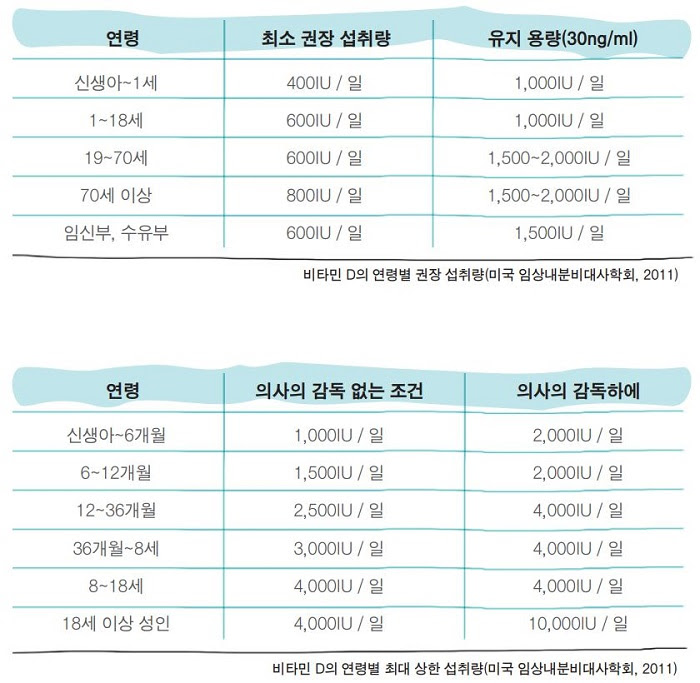


![[Vitamin D Episode 3] How Much Vitamin D Should You Take? | Dr. Esther Yeo](http://esther-mall.com/cdn/shop/articles/48_1eff4f00-eade-4a65-88e7-535ee268a33f.jpg?v=1734116775&width=480)


Comments (0)
There are no comments for this article. Be the first one to leave a message!