Pharmacist who reads papers
Introducing selenium, a miracle element that catches free radicals.
1. Antioxidants2
. Anti-inflammatory
. Anti-inflammatory
3. Thyroid hormone metabolism
Hello. I'm a pharmacist Jinny.
What do Kamut rice, which recently became a hot topic as a super grain in ancient Egypt, and Brazil nut, which is hailed as the most perfect fruit on earth, have in common? It is rich in the antioxidant mineral selenium.
Selenium was initially stigmatized as a toxic substance and forgotten for over 100 years, but it wasn't until the 1970s that it was discovered to be an essential component of antioxidant enzymes in the body. Since then, research on selenium has been in full swing, and in 1978, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) recognized selenium as an "essential mineral" that must be consumed, earning it the honorary nickname of "the miracle element, the dream element, and the blue wizard."
Selenium was initially stigmatized as a toxic substance and forgotten for over 100 years, but it wasn't until the 1970s that it was discovered to be an essential component of antioxidant enzymes in the body. Since then, research on selenium has been in full swing, and in 1978, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) recognized selenium as an "essential mineral" that must be consumed, earning it the honorary nickname of "the miracle element, the dream element, and the blue wizard."
In today's paper, we'll take a look at how important selenium plays in the body.
1. Antioxidants
Antioxidants are the body's defense system against free radicals that are constantly produced and attack the human body as long as they live.The selenium we consume is a component of various antioxidant enzymes in the body, which are called selenium-dependent enzymes. Glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which is the body's representative antioxidant enzyme that protects cell membranes from free radicals, is also a selenium-dependent enzyme.
A review paper published in Environmental health and preventive medicine in 2008 summarized the antioxidant activity of selenium as follows [1].
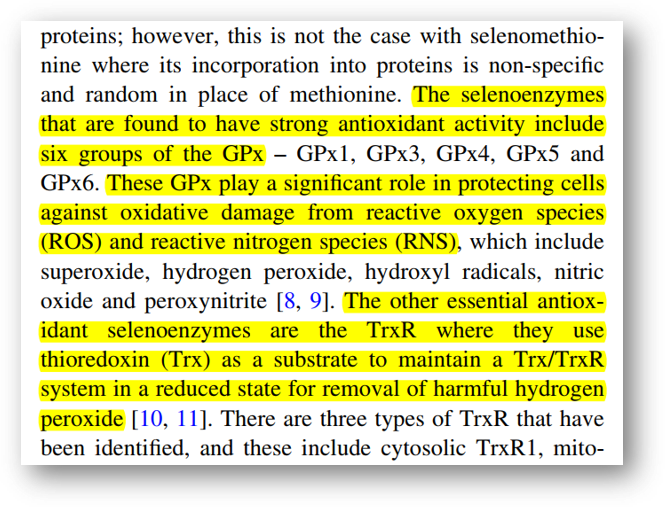
"Selenium-dependent enzymes that have been shown to have potent antioxidant activity include six groups of GPx. These GPx play an important role in protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). Another essential antioxidant selenium-dependent enzyme is TrxR (thioredoxin reductase), which uses thioredoxin as a substrate to remove harmful hydrogen peroxide, keeping the Trx/TrxR system reduced."
2. Anti-inflammatory
Essentially, inflammation is considered part of the immune system as the body's natural defense response to harmful stimuli such as pathogens or injury. However, if the mechanisms that cause and inhibit inflammation are not precisely controlled, it can lead to inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Therefore, when it comes to the prevention and treatment of inflammatory diseases, the scientific community is looking for ways to inhibit the excessive activity of NF-kappaB, which is called the master switch of inflammation.
Let's take a look at a review paper published in Hormone and Metabolic Research in 2009 on selenium's anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
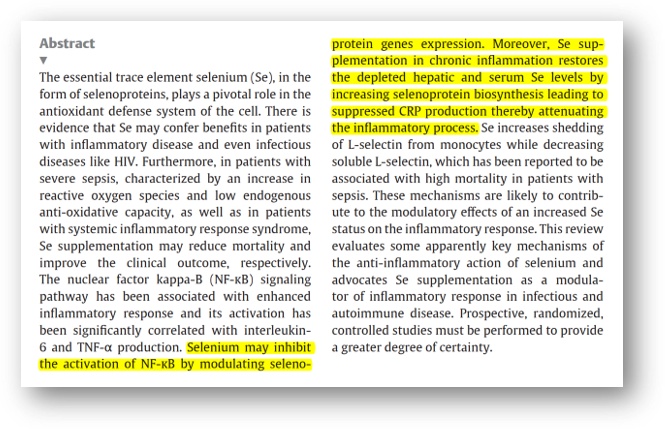
"Selenium can inhibit the activation of NF-kappaB by regulating selenoprotein (selenium-containing protein) gene expression. In addition, in chronic inflammation, selenium supplementation increases the biosynthesis of selenoprotein, thereby inhibiting the production of CRP (a marker of acute inflammation, a marker of infection), thereby restoring depleted liver and serum selenium levels, thereby relieving the inflammatory process."
3. Thyroid hormone metabolism
The thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland in our body, which makes and stores thyroid hormones and secretes them into the blood. Thyroid hormones play a very important role in boosting the body's metabolic processes and maintaining body temperature through the heat generated during this process. But did you know that selenium is essential for the metabolism of thyroid hormones?
A 2001 review paper published in Nutrition & Food Science examined the role of selenium in thyroid hormone metabolism and reported that [3]:

"Over the past decade, selenium has been shown to be an essential component of type 1 oidothyronine 5′-deiodinating enzyme, which converts thyroxine (T4) into the more biologically active hormone 3, 5, and 3'-
triiodothyronine (T3)."
Today, we're going to look at the very important actions that selenium performs in the body, and its status as an essential nutrient. According to the Korean Nutritional Intake Guidelines, the recommended daily intake of selenium for adult men and women is about 55μg, so it is recommended to pay close attention to your eating habits and supplement if necessary.
I hope you have a healthy day in body and mind. It was Jinny.
[1] Tinggi U. (2008). Selenium: its role as antioxidant in human health. Environmental health and preventive medicine, 13(2), 102–108.
[2] Duntas LH. (2009). Selenium and inflammation: underlying anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Horm Metab Res, 41(6), 443-7.
[3] Citation Ünüsan, N. (2001). Selenium and thyroid hormone metabolism. Nutrition & Food Science, 31(2), 91-95.
[2] Duntas LH. (2009). Selenium and inflammation: underlying anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Horm Metab Res, 41(6), 443-7.
[3] Citation Ünüsan, N. (2001). Selenium and thyroid hormone metabolism. Nutrition & Food Science, 31(2), 91-95.


![[Selenium Efficacy] Introducing selenium, a miracle element that catches free radicals](http://esther-mall.com/cdn/shop/articles/45.jpg?v=1734020583&width=480)
![[Rosemary Extract Complex (SunMax) Benefits] Wrinkle Improvement? 3 Benefits of Rosemary Extract](http://esther-mall.com/cdn/shop/articles/44.jpg?v=1734007042&width=480)
![[Proteoglycan Benefits] 3 Benefits of Proteoglycans, the true constituents of cartilage](http://esther-mall.com/cdn/shop/articles/46.jpg?v=1734020926&width=480)