Chondroitin sulfate, which helps improve osteoarthritis symptoms.

Hello. I'm a pharmacist Jinny.
When it comes to joint health, the most well-known ingredient in Korea at the moment is definitely chondroitin. Chondroitin is a type of glycosaminoglycan that makes up tissues such as skin and cartilage, and one of the sugars that make up chondroitin is a sulfate ester called chondroitin sulfate, or chondroitin sulfate; CS).
Chondroitin sulfate is a bioactive substance present in joints and cartilage, and is known to nourish joints and cartilage, inhibit chondrolytic enzymes, and promote the formation of new cartilage [1]. The European Union of Rheumatologists (EULAR) strongly recommended chondroitin sulfate for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee in 2003 [2].
As a result, the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety has also recognized the joint and cartilage health functions of some ingredients containing chondroitin sulfate. Typical ingredients include chondroitin sulfate and protein, which contain mucopolysaccharides and proteins.
Now, let's take a look at the benefits of taking chondroitin sulfate, whether it is recommended as an adjuvant for the treatment of osteoarthritis, and whether its functionality is recognized by the Food and Drug Administration.
Osteoarthritis, also called degenerative joint disease or degenerative arthritis, is an inflammatory disease of the joints that manifests itself with the highest frequency. It is a disease in which the bones, joint membranes, and surrounding ligaments are secondary damage due to gradual damage or degenerative changes in the articular cartilage, which absorbs shock between the bones that make up the joint, causing pain, deformity, and dysfunction [3].
It occurs according to factors such as age, gender, genetic factors, obesity, and specific joint areas without a specific cause, and occurs in more than 60% of people over 65 years of age, and it occurs in more than 60% of people over the age of 65. Hands · It manifests itself mainly in the hip joint. The main symptom is pain in the joint area, which significantly affects the quality of life. Despite this common condition, there are no definitive medications that can prevent or treat osteoarthritis [4].
For this reason, the scientific community is testing various possibilities, and chondroitin sulfate has been extensively studied as an ingredient that can help with osteoarthritis. In 2019, Honvo and researchers conducted a comprehensive review of 18 studies with a total of 3,791 participants to evaluate the effects of chondroitin sulfate intake on osteoarthritis. This study suggests that chondroitin sulfate supplementation may be superior to placebo in the management of osteoarthritis and may help improve pain [5].

"Three- and 12-month intake of chondroitin sulfate had a positive effect on both pain and functional status in patients with osteoarthritis. ... The benefits were maintained when co-administered with NSAIDs. However, chondroitin sulfate alone has shown a greater effect, and the benefit of chondroitin sulfate in improving pain may be stronger than previously reported in previous studies."
Earlier, I mentioned that there is no definitive drug that can prevent or treat osteoarthritis. However, there are many people who take prescribed medications for arthritis. Most medicines are used to reduce pain and reduce inflammation caused by osteoarthritis, most notably nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). However, there is a burden associated with long-term use of these medications.
That's why academics are designing trials that compare NSAIDs with ingredients that are thought to help improve osteoarthritis. One of the most prominent of these studies is GAIT.
This study evaluated the effects of glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, and the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) celecoxib in 1,583 patients with knee osteoarthritis. This study reported a significant improvement in edema in patients with pre-existing joint edema who took chondroitin sulfate compared to placebo [6].
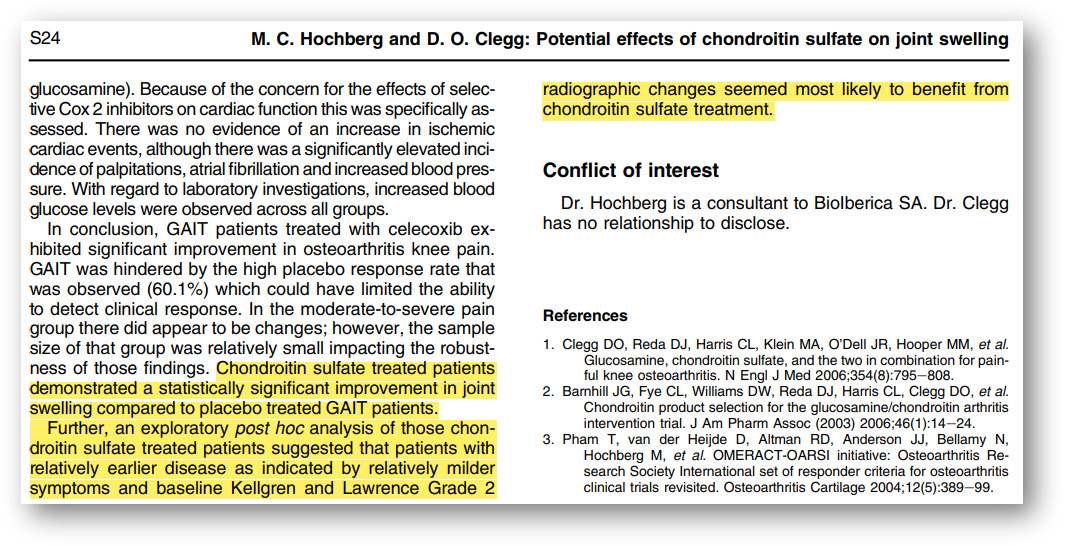
"There was a significant improvement in joint edema in the chondroitin sulfate group compared to the control group. Exploratory post-hoc analysis suggests that earlier patients are more likely to benefit from chondroitin sulfate supplementation."
3. Improves exercise capacity in patients with osteoarthritis
The main symptom of osteoarthritis is localized pain in the joint area, but there are also other symptoms such as decreased range of motion and swelling of the joint. In addition, if the joint surface becomes irregular due to loss and degeneration of cartilage, you may feel a friction sound when moving the joint. In addition, muscle atrophy can occur, so muscle strengthening and restoring joint range of motion are important to reduce joint load.
However, it is also true that exercise becomes increasingly difficult depending on the symptoms of osteoarthritis, so when evaluating ingredients that may help improve osteoarthritis, the extent to which it affects the improvement of exercise performance is also an important variable.
Chondroitin sulfate, which may be beneficial for osteoarthritis, has also been evaluated for its benefits on the exercise capacity of osteoarthritis patients. Uebelhart and the colleagues (1998) evaluated the effects of chondroitin sulfate intake on 42 patients with knee osteoarthritis and reported that chondroitin sulfate supplementation showed an improvement in overall exercise performance [7].

"This study found that chondroitin sulfate was well tolerated, significantly improved pain, and increased overall exercise capacity. … These results suggest that chondroitin sulfate is an effective, safe, and slow-acting component in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis."
Today, we looked at the results of academic research on chondroitin sulfate, the active ingredient in chondroitin, which is attracting attention as a joint health ingredient. It has been extensively tested in patients with osteoarthritis for quite a long time, and most studies have shown consistent benefits, so it is worth considering as an adjunctive treatment if you have osteoarthritis.
In addition, Morreale et al. (1996), who evaluated the effects of NSAIDs and chondroitin sulfate in 146 patients with knee osteoarthritis, reported that the effects of NSAIDs were immediate and obvious, but the effects disappeared when discontinuation occurred, while those taking chondroitin sulfate experienced slower improvement but maintained improvement for up to 3 months after discontinuation [8].
Considering this, we can expect long-term impact on chondroitin sulfate as an adjuvant treatment rather than an immediate effect. In addition, all of the human body application tests introduced today are tests that treat 'chondroitin sulfate' rather than chondroitin, so it is recommended that you check whether it is a functional ingredient containing 'chondroitin sulfate' when purchasing the product. As mentioned earlier, 'mucopolysaccharide/protein' is a functional ingredient whose content of chondroitin sulfate has been verified, so you can easily check it by looking at whether 'mucopolysaccharide/protein' is written in the name of the functional ingredient.
I hope you have a healthy day in body and mind. It was Jinny.
[1] Society for Biochemical and Molecular Biology, Encyclopedia of Biochemistry <Chondroitin Sulfate>
[2] Uebelhart, D. (2008). Clinical review of chondroitin sulfate in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 16, S19-S21.
[3,4] Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, National Health Information Portal Medical Information <Osteoarthritis>
[5] Honvo, G., Bruyere, O., Geerinck, A., Veronese, N., & Reginster, J. Y. (2019). Efficacy of chondroitin sulfate in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a comprehensive meta-analysis exploring inconsistencies in randomized, placebo-controlled trials. Advances in therapy, 36(5), 1085-1099.
[6] Hochberg, M. C., & Clegg, D. O. (2008). Potential effects of chondroitin sulfate on joint swelling: a GAIT report. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 16, S22-S24.
[7] Uebelhart, D., Eugene, J. M. T., Delmas, P. D., Chantraine, A., & Vignon, E. (1998). Effects of oral chondroitin sulfate on the progression of knee osteoarthritis: a pilot study. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 6, 39-46.
[8] Morreale, P., Manopulo, R., Galati, M., Boccanera, L., Saponati, G., & Bocchi, L. (1996). Comparison of the antiinflammatory efficacy of chondroitin sulfate and diclofenac sodium in patients with knee osteoarthritis. The Journal of rheumatology, 23(8), 1385-1391.


![[Chondroitin sulfate effect] from pain, swelling, and exercise ability to improvement, 3 benefits of chondroitin for osteoarthritis](http://esther-mall.com/cdn/shop/articles/a89513f8e056783b190_520x500_18fb2bc0-3c95-4a2c-bac1-22bbb18c07c8.jpg?v=1734621870&width=480)
![[Omega-3 Benefits] From blood circulation health to improving dry eye syndrome, the benefits of omega-3](http://esther-mall.com/cdn/shop/articles/4d9919c795a3af6f507_520x500_efc7d197-695e-4bd2-9e28-c299adf7cdc9.jpg?v=1734621837&width=480)
